
Wrist drop or foot drop: Once the muscle is injured, it heals through fibrosis.Walking is impaired when leg muscles are affected. In the forearm, the person may be unable to grip objects. Disability: As muscle is the first structure to be affected, inability to perform a particular movement is noticed quite early.For an appointment call Naas Physio Clinic on: (045) 874 682Ĭomplications of acute compartment syndrome Pressures more than 30 mmHg are considered diagnostic of acute compartment syndrome.Ĭhronic compartment syndrome occurs when intra compartment pressure is more than 15 mm Hg at rest, 30mmHg one minute post exercise and more than 20 mmHg 5 minutes post exercise. Normal compartment pressures range between 8mmHg to 10mmHg. Measuring compartment pressure every hour after an injury is a reliable method to detect onset of compartment syndrome. Overtraining or poorly spaced out tournaments.Running on a concrete track instead of running track.Playing on artificial turf instead of regular grass turf.Repeated limb movement as in running or cycling.Sustained awkward body positions during long surgeries (gynaecology)Ĭhronic compartment syndrome may be caused by:.
MYOFASCIA COMPARTMENTS OF LEG SKIN
Symptoms of acute compartment syndrome include: The symptoms of compartment syndrome arise as a result of vascular compromise that affects muscle tissue. What are the symptoms of compartment syndrome? Resting and switching to an alternate activity helps to resolve the symptoms. This occludes the blood vessels reducing normal blood supply. The inelastic fibrous sheath that surrounds the muscle does not stretch as the muscle enlarges. Similarly, nerves can tolerate ischemia up to 1 hour but undergo irreversible damage 8 hours after injury.Ĭhronic compartment syndromeoccurs when the muscle volume increases after a prolonged activity. But complete cell death occurs after 8 hours. A muscle can resist poor blood supply up to 4 hours after injury. This needs to be done immediately to avoid permanent muscle or nerve damage. Decompression surgery to cut open the fascia is done to relieve the pressure. There are two types of compartment syndromes:Īcute compartment syndrome (ACS)is a medical emergency that occurs after an injury. Ross Allen is a former Ireland Rugby & County Football Player Types of compartment syndrome For an appointment call Naas Physio Clinic on: (045) 874 682Ĭompartment Syndrome. But compartment syndrome can occur in hands, arms, thighs, abdomen and back. The muscles in leg and forearm are more affected. The muscles that bend the thumb and fingers (flexor pollicis longus and profundus) are most commonly affected in the compartment syndrome of forearm. The muscle belly is more vulnerable to ischemia. This leads to ischemia (cell death due to lack of oxygen) and contracture of the muscles.

Lack of oxygen and fresh nutrients affects normal muscle function. Within a few hours, the blood supply to the muscles is compromised. Consequently, more fluid oozes out of the blood vessels into the intracellular spaces. The flow of blood from arteries to veins is impeded.
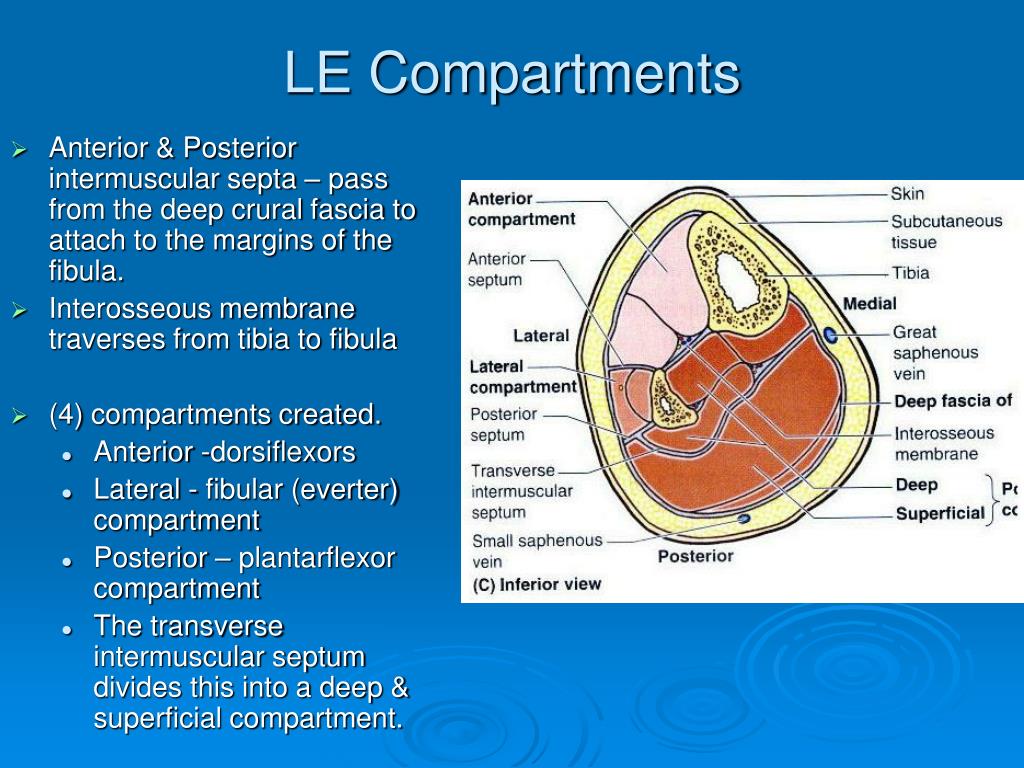
This raises pressure within the compartment. Elevated fluid levels press other structures against the inelastic fascia. When there is an injury to a body part, bleeding or swelling occurs. The nerves are affected much later by reduced blood supply. Muscles are the primary target in compartment syndrome. An increase in the intra-compartmental pressure due to external or internal reasons is termed as compartment syndrome. The fascia that separates one compartment from another is tough and inelastic. Each compartment also has nerves and blood vessels. The muscles in our body are enclosed by a soft tissue sheet (fascia) to form separate compartments. COMPARTMENT SYNDROME What is compartment syndrome?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
